Workshop Resources
December 10, 2025
Building confident and independent thinkers through reflective, response-based writing.
“Today, we continue our work with response-based writing by looking closely at how building prior knowledge strengthens students’ understanding and deepens the quality of their responses.”
Join the Conversation
-

Artivist Storywalk Whiteboard
Whiteboard sharing StoryWalk responses. Grounding the work in purpose and claim.
-

Preparing Students to Read Whiteboard
Whiteboard with responses answering the question: “How do you prepare students to read a piece of text?”
-

Writing Sample Observations
Observations from discussion rounds for writing samples. Answering the questions: 1.) What were the strengths we saw in our writing responses? 2.) How can we model writing in front of students? 3.) A great student claim has… and 4.) What “counts” as evidence in my subject area?
Access all of the workshop handouts.
Need Nonfiction Resources for your classroom?
-
NewsELA
National Geographic Kids
Time for Kids
Ted-Ed
Epic Kids!
And more!
-
Infographic Prompts
Biographies
Current Events
History, Math, Science, and more
-
All subject areas
Image analysis
Storywalk and Learning Log activities
-
Nonfiction Reading
Disciplinary Literacy
Argumentative Writing
Nonfiction Writing Resources
Tools like PrintFriendly (clean print from digitial sources) and Brisk (lexile articles)
-
Grab Ready-to-Use Handouts
Double-Entry Learning Log (Input and Elaboration)
Triple-Entry Learning Log (Input, Elaboration, & Application)
Nonfiction Summary Writing with FACTS
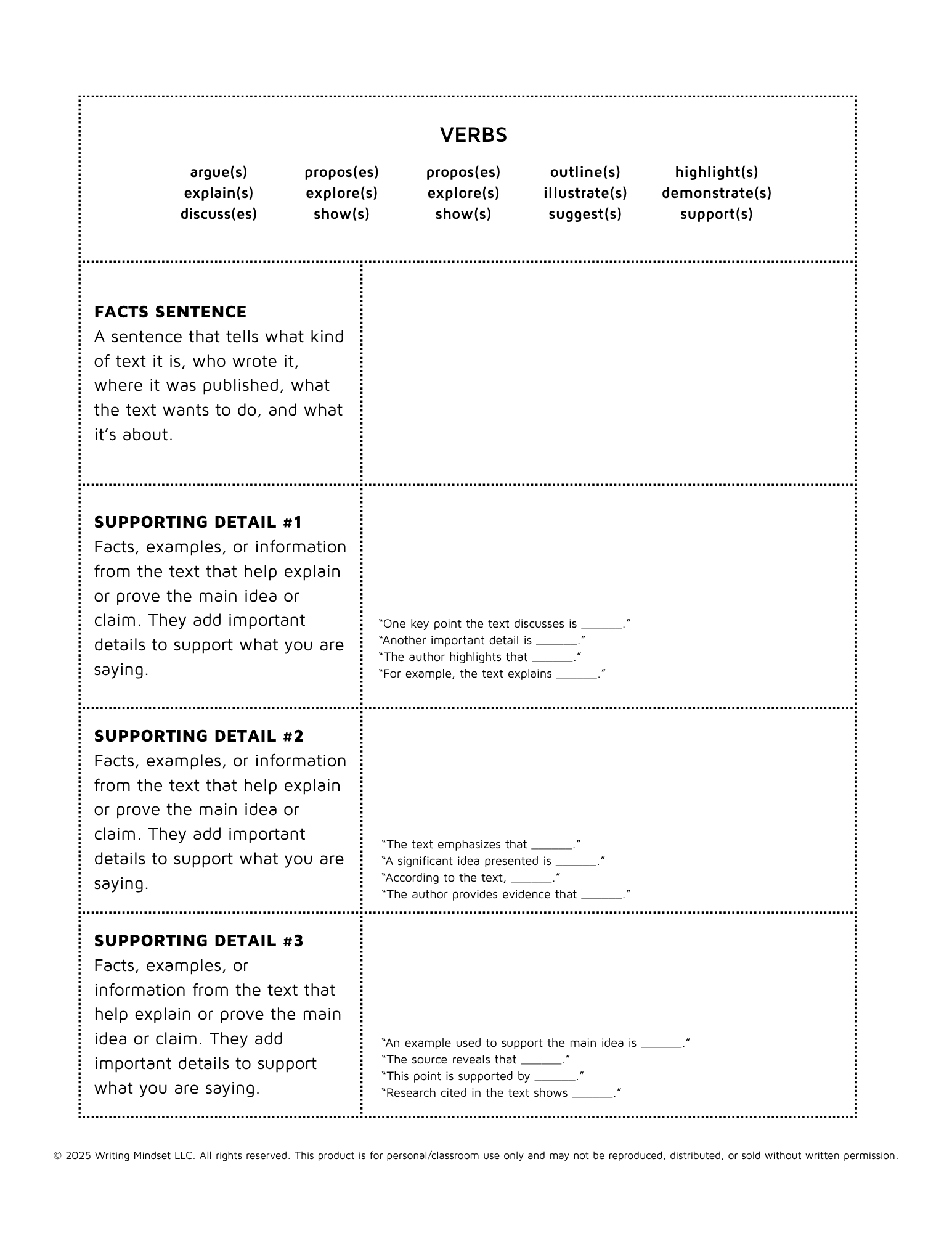
CER Response Writing with FACTS
VIDEO RESOURCE
WATCH NOW: Get an introduction and examples of learning logs here.
Need a Grades 6–8 Nonfiction Summary Response Writing Rubric
Click the link to make it your own.
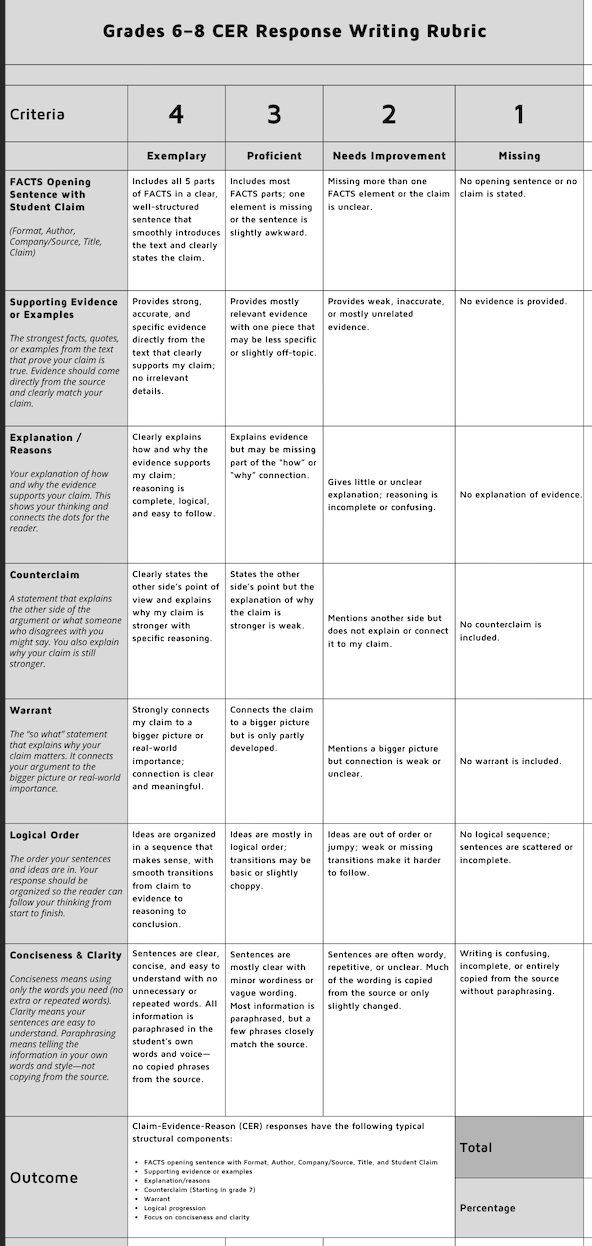
Need a Grades 6–8 CER Response Writing Rubric
Click the link to make it your own.
References & Inspiration
Anderson, C., & Ray, K. W. (2018). A teacher’s guide to writing conferences. grades K-8. Heinemann.
Applebee, A. N., & Langer, J. A. (2011). EJ Extra: A snapshot of writing instruction in middle schools and high schools [free access]. English Journal, 100(6), 14–27. https://doi.org/10.58680/ej201116413
Beers, K., & Probst, R. E. (2016). Reading nonfiction: Notice & note stances, signposts, and strategies. Heinemann.
Burke, J. (2019). The 6 academic writing assignments: Designing the user’s journey. Heinemann.
Cappiello, M. A., & Dawes, E. T. (2023). Text sets in action: Pathways through content area literacy. Routledge.
College Entrance Examination Board. (2003). The Neglected “R”: The Need for a Writing Revolution. Report of The National Commission on Writing in America’s Schools and Colleges. New York, New York.
Culham, R. (2010). Traits of writing: The Complete Guide for Middle School. Scholastic.
Emdin, C. (2021). Ratchetdemic: Reimagining academic success. Beacon Press.
Ewoldt, K. B., & Morgan, J. J. (2017). Color-coded graphic organizers for teaching writing to students with learning disabilities. TEACHING Exceptional Children, 49(3), 175–184. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040059916681769
France, P. E. (2025). My Kids Can’t Write, K–5: How to Advance Achievement Through Cross‑Curricular Writing (1st ed.) Corwin.
Gallagher, K. (2023). In the best interest of students: Staying true to what works in the Ela Classroom. Routledge.
Gallagher, K. (2025). To read stuff you have to know stuff: Helping students build and use prior knowledge. Heinemann.
Gallagher, K., & Kittle, P. (2018). 180 days: Two teachers and the quest to engage and empower adolescents. Heinemann.
Graham, S., & Perin, D. (2007). Writing next: Effective strategies to improve writing of adolescents in middle and high schools – A report to Carnegie Corporation of New York. Washington, DC:Alliance for Excellent Education.
Graham, S., Bruch, J., Fitzgerald, J., Friedrich, L., Furgeson, J., Greene, K., Kim, J., Lyskawa, J., Olson, C.B., & Smither Wulsin, C. (2016). Teaching secondary students to write effectively (NCEE 2017-4002). Washington, DC: National Center for Education Evaluation and Regional Assistance (NCEE), Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education. Retrieved from the NCEE website: http://whatworks.ed.gov.
Hammond, Z., & Jackson, Y. (2015). Culturally responsive teaching and the brain: Promoting authentic engagement and rigor among culturally and linguistically diverse students. Corwin, a SAGE Company.
Harper, R. G. (2022). Write now & write on, grades 6-12: 37 strategies for authentic daily writing in every content area. Corwin Literacy.
Harvey, S., & Goudvis, A. (2017). Strategies that work : teaching comprehension for understanding, engagement, and building knowledge, grades K-8 (3rd ed.). Routledge.
Heard, G., & Nye, N. S. (2024). Awakening the heart: Teaching poetry, K-8. Heinemann.
Hochman, J., Wexler, N., Maloney, K., & Lemov, D. (2024). The writing revolution 2.0: A guide to advancing thinking through writing in all subjects and grades. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Jackson, J. (2014). How to teach students to critically think about text: 15 easy to follow techniques for the K-12 teacher. Jackson Consulting, Inc.
Jackson, J. (2016). How to teach students to write informational text: A deconstructed, step-by-step approach to teaching k-12 students to write. Jackson Consulting, Inc.
Jetton, T. L., & Shanahan, C. (2012). Adolescent literacy in the academic disciplines: General principles and practical strategies. The Guilford Press.
Lent, R. C. (2016). This is disciplinary literacy: Reading, writing, thinking, and doing . . . content area by content area. Corwin Press.
Lent, R. C., & Voigt, M. (2019). Disciplinary literacy in action: How to create and sustain a school-wide culture of deep reading, writing, and thinking. Corwin Press.
Moje, E. B., & Sutherland, L. M. (2003). The Future of Middle School Literacy Education. English Education, 35(2), 149–164. https://doi.org/10.58680/ee20031634
Muhammad, G. (2021). Cultivating genius: An equity framework for culturally and historically responsive literacy. Scholastic.
Muhammad, G. (2023). Unearthing joy: A guide to culturally and historically responsive curriculum and instruction. Scholastic Professional.
Olson, C. B., & Land, R. (2007). A cognitive strategies approach to reading and writing instruction for English language learners in secondary school. Research in the Teaching of English, 41(3), 269–303. https://doi.org/10.58680/rte20076014
Prather, L. (2019). Story matters: Teaching teens to use the tools of narrative to argue and inform. Heinemann.
Sedita, J. (2023). The writing rope: A framework for explicit writing instruction in all subjects. Paul H. Brookes Publishing Co.
SHANAHAN, T., & SHANAHAN, C. (2008). Teaching disciplinary literacy to adolescents: Rethinking content- area literacy. Harvard Educational Review, 78(1), 40–59. https://doi.org/10.17763/haer.78.1.v62444321p602101
Tokuhama‑Espinosa, T., Nazareno, J. R. S., & Rappleye, C. (2024). Writing, Thinking, and the Brain: How neuroscience can improve writing instruction. Teachers College Press.